Peripheral Neuropathy
Have you experienced a lack of muscle control, increased sensitivity to touch, or numbness? Welcome to our comprehensive blog on peripheral neuropathy. This is a complex and multifaceted condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Our mission is to provide you with the latest information, research, and expert insights into the causes, symptoms, and treatments.
We will explore its various forms and investigate the underlying factors and potential triggers. It also lists some effective strategies for managing and alleviating its impact on daily life.
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
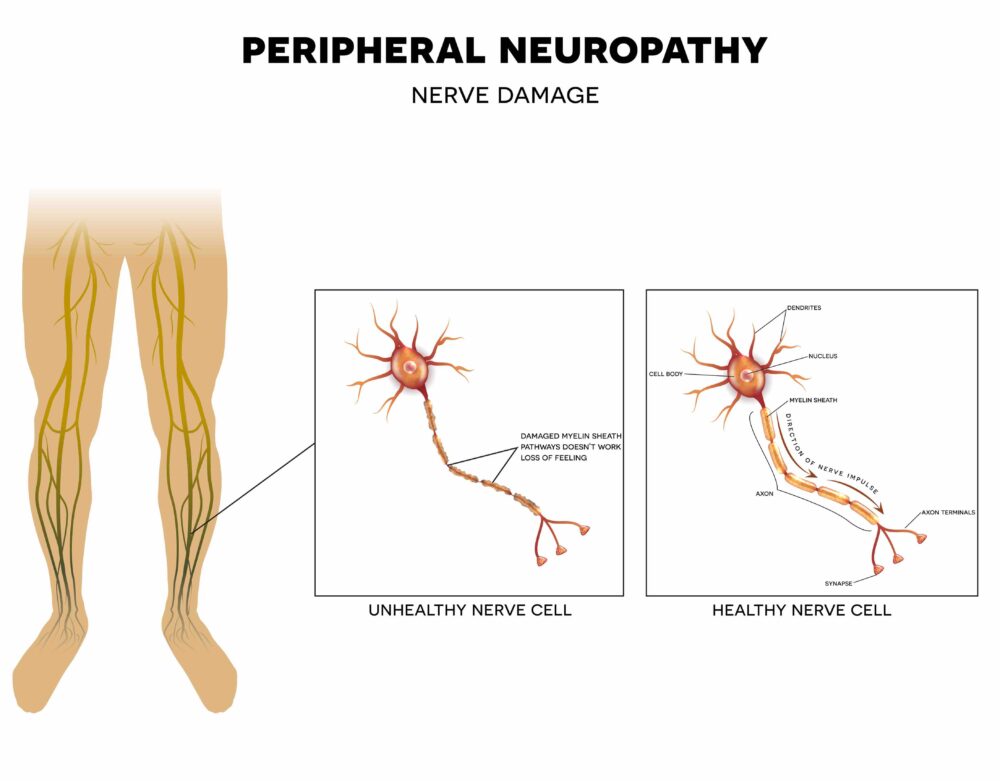
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition involving damage to the peripheral nervous system. This system is a vast communications network that sends signals between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and all other parts of the body.
It is a result of damage to the nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord (peripheral nerves), causing weakness, numbness, and pain in the hands and feet. It can also affect other areas and body functions such as digestion, urination, and circulation.
Some of the common peripheral neuropathies include the following:
- Diabetic neuropathy is caused by damage to the nerves due to high blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
- Charcot-Marie-tooth disease is a progressive illness that causes muscle weakness, numbness, and tingling in the hands, feet, and lower legs.
- Guillain-Barre syndrome is an autoimmune disorder affecting the peripheral nerves. This starts in the feet and legs and can spread to the upper body.
- Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy is a side effect of chemotherapy drugs used to treat cancer.
- HIV-related neuropathy. This type affects people with HIV indicating advanced HIV infection.
What are the Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy?
- Gradual onset of numbness, prickling, or tingling in the feet or hands spreading upward into the legs and arms.
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing, or burning pain in the feet or hands.
- Extreme sensitivity to touch.
- Loss of coordination and falling.
- Muscle weakness, especially in the feet or hands.
- Inability to feel pain, pressure, or temperature changes.
- Lack of muscle control or twitching.
- Bowel or bladder problems.
- Dizziness or light-headedness.
- Sexual dysfunction.
How Can I Prevent Peripheral Neuropathy?
The most vital thing is to control your blood sugar levels. This will help prevent nerve damage from developing in your body. Suppose you have type 2 diabetes; try eating foods high in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids. These foods will help to lower cholesterol levels and inflammation and thus; protect against heart disease.
Other preventive measures include:
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
- Correcting vitamin deficiencies
- Eating a healthy diet
- Losing weight
- Avoid toxins
- Doing regular exercises
What Causes Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is caused by damage to the peripheral nerves. This can result from a variety of factors. The common factor is diabetes, which causes nerve damage due to high blood sugar levels over time.
High blood glucose and fat levels in the blood from diabetes can damage the nerves and the small blood vessels nourishing them. This leads to peripheral neuropathy.
Smoking, excessive drinking, and high blood pressure are also risk factors for diabetes-related neuropathy.
Diabetes-related neuropathy is nerve damage caused by elevated blood sugar. High blood glucose causes chemical alteration in nerves. This impairs the nerves’ ability to transmit signals. It can also damage blood vessels carrying oxygen and nutrients to the nerves.
How Can You Test for Peripheral Neuropathy?
There are several ways to test for peripheral neuropathy. However, the initial step is a thorough physical examination of your medical history and symptoms. Meanwhile, the test is:
- Blood tests: These tests can identify possible underlying causes of neuropathy, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiencies.
- Imaging tests: MRI or CT scans can help detect nerve damage, inflammation, or tumors causing neuropathy.
- Nerve function tests: Nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG) are used to measure nerve function and diagnose neuropathy.
What is a Nerve Conduction Test (NCS)?
A nerve conduction study (NCS) is a non-invasive diagnostic that measures the speed and strength of electrical signals in your nerves. During the test, electrodes are placed on your skin near the affected nerves.
A small electrical current is applied to stimulate the nerves. The response is recorded. The data obtained from these tests can help determine the extent of nerve damage and pinpoint the specific nerves involved.
Treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy
Your healthcare provider may recommend one or more of the following approaches:
- Medication: Pain relievers, anti-seizure medications, and antidepressants can help alleviate neuropathic pain.
- Topical treatments: Over-the-counter creams and patches containing capsaicin or lidocaine offer temporary relief.
- Physical therapy: Exercises and stretches can improve muscle strength, mobility, and balance, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing stress can help improve overall health to reduce neuropathy symptoms.
Contact Us to Get Tested for Peripheral Neuropathy!
It is not just about walking, it is about getting back to the activities you love. Suppose you are ready to get back in the game; we can help. If you have neuropathy, make sure to take care of your feet every day, which can save your feet in the future!
Our team has over 25 years of experience helping people with peripheral neuropathy get their lives back. We have helped thousands of people with peripheral neuropathy regain their mobility, strength, and independence.
That is why Burlington County Foot & Ankle Associates can help you understand your condition, determine appropriate treatment options, and develop a personalized recovery plan. Please get in touch with our office today by calling 609-714-0052, or by filling out our online contact form to schedule your appointment.
FILL OUT THE FORM TO
CONTACT US
© Burlington County Foot & Ankle, Assoc., Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
Web Design by CP Solutions.
Marketed by VMD Services.